Joint replacement devices have revolutionized the treatment of joint-related conditions, offering relief to millions of people suffering from debilitating joint pain and limited mobility. These devices are designed to restore function and alleviate pain in damaged or diseased joints, allowing patients to regain their mobility and quality of life. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the world of joint replacement devices, including their types, benefits, surgical procedures, and postoperative care.
Understanding Joint Replacement Devices
1. Description:
- Joint replacement devices, also known as prosthetic joints, are artificial implants used to replace damaged or diseased joints.
- They are designed to mimic the function of natural joints, restoring mobility and alleviating pain for patients suffering from conditions such as arthritis, degenerative joint disease, and traumatic injury.
2. Components:
- Joint replacement devices consist of two main components: the implant and the articulating surface.
- The implant is typically made of metal, ceramic, or plastic and is inserted into the bone to replace the damaged joint.
- The articulating surface is the part of the implant that comes into contact with the opposing bone, allowing for smooth movement and function.
3. Types:
- There are several types of joint replacement devices, including:
- Total hip replacement (THR)
- Total knee replacement (TKR)
- Total shoulder replacement
- Partial knee replacement
- Partial hip replacement
- Reverse shoulder replacement
Types of Joint Replacement Devices
1. Total Hip Replacement (THR):
- Description: Total hip replacement involves replacing the entire hip joint with an artificial implant.
- Components: The implant consists of a metal or ceramic ball that is attached to a stem, which is inserted into the femur, and a cup that is implanted into the pelvis.
- Benefits: THR can relieve pain, improve mobility, and restore function in patients with conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and hip fractures.
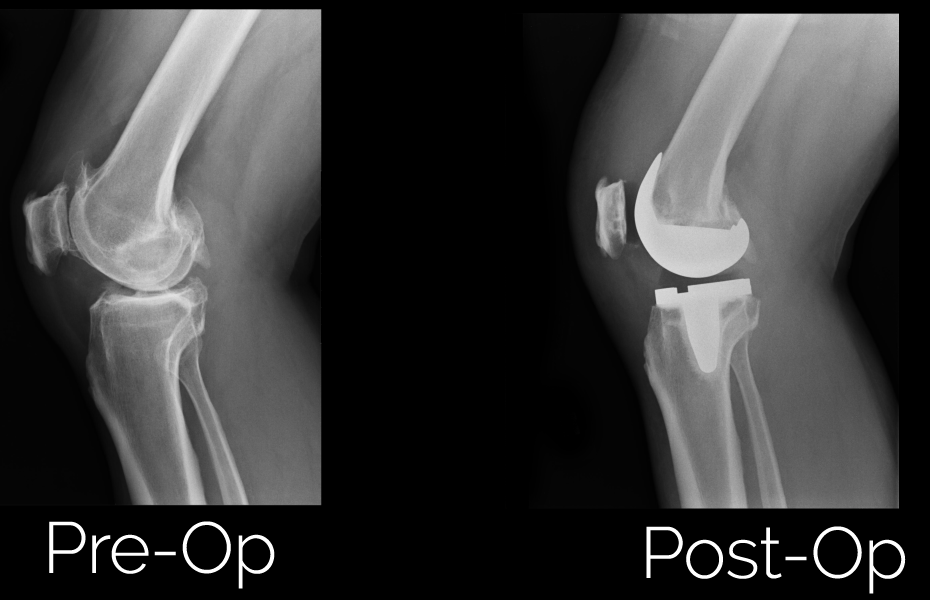
2. Total Knee Replacement (TKR):
- Description: Total knee replacement involves replacing the entire knee joint with an artificial implant.
- Components: The implant consists of metal components that are attached to the femur and tibia, as well as a plastic spacer that serves as the articulating surface.
- Benefits: TKR can relieve pain, improve mobility, and restore function in patients with conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and knee injuries.
3. Total Shoulder Replacement:
- Description: Total shoulder replacement involves replacing the entire shoulder joint with an artificial implant.
- Components: The implant consists of a metal ball that is attached to the humerus and a plastic socket that is implanted into the scapula.
- Benefits: Total shoulder replacement can relieve pain, improve mobility, and restore function in patients with conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and rotator cuff tears.
4. Partial Knee Replacement:
- Description: Partial knee replacement involves replacing only the damaged or diseased parts of the knee joint with an artificial implant.
- Components: The implant consists of metal components that are attached to the femur and tibia, as well as a plastic spacer that serves as the articulating surface.
- Benefits: Partial knee replacement can relieve pain, improve mobility, and restore function in patients with localized arthritis or cartilage damage.
5. Partial Hip Replacement:
- Description: Partial hip replacement involves replacing only the damaged or diseased parts of the hip joint with an artificial implant.
- Components: The implant consists of a metal or ceramic ball that is attached to a stem, which is inserted into the femur, and a plastic cup that is implanted into the pelvis.
- Benefits: Partial hip replacement can relieve pain, improve mobility, and restore function in patients with conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and hip fractures.
6. Reverse Shoulder Replacement:
- Description: Reverse shoulder replacement involves reversing the normal anatomy of the shoulder joint, with the ball portion of the joint being placed on the scapula and the socket portion being placed on the humerus.
- Components: The implant consists of a metal ball that is attached to the scapula and a plastic socket that is implanted into the humerus.
- Benefits: Reverse shoulder replacement can relieve pain, improve mobility, and restore function in patients with conditions such as rotator cuff tears, severe arthritis, and failed previous shoulder surgery.
Surgical Procedure
1. Preoperative Evaluation:
- Before undergoing joint replacement surgery, patients undergo a thorough preoperative evaluation, which may include:
- Physical examination
- Imaging studies (X-rays, MRI, CT scan)
- Blood tests
- Cardiac evaluation
2. Anesthesia:
- Joint replacement surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia or regional anesthesia, such as spinal or epidural anesthesia.
- The choice of anesthesia depends on the patient’s overall health, the type of joint being replaced, and the surgeon’s preference.
3. Incision:
- The surgeon makes an incision over the affected joint, exposing the damaged or diseased joint surfaces.
4. Removal of Damaged Tissue:
- The damaged or diseased joint surfaces are removed using specialized surgical instruments, such as saws, drills, and chisels.
5. Implant Placement:
- The artificial implant is then inserted into the bone, either by cementing it in place or by press-fitting it into the bone.
6. Closure:
- The incision is closed with sutures or staples, and a sterile dressing is applied to the wound.
Postoperative Care
1. Pain Management:
- Patients are given pain medication to help manage postoperative pain and discomfort.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), opioids, and local anesthetics may be used for pain management.
2. Physical Therapy:
- Physical therapy is an essential part of the recovery process after joint replacement surgery.
- Physical therapists work with patients to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the affected joint.
3. Rehabilitation:
- Patients are encouraged to start moving and using the affected joint as soon as possible after surgery.
- Rehabilitation exercises and activities help patients regain mobility and function in the replaced joint.
4. Follow-Up Visits:
- Patients are scheduled for follow-up visits with their surgeon to monitor their progress and address any concerns or complications.
- X-rays may be taken to assess the position and stability of the implant.
5. Lifestyle Modifications:
- Patients may need to make lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding high-impact activities and maintaining a healthy weight, to protect their new joint and prevent complications.
Advantages of Joint Replacement Devices
1. Pain Relief:
- Joint replacement devices can provide significant pain relief for patients suffering from chronic joint pain and arthritis.
2. Improved Mobility:
- Joint replacement devices can improve mobility and function in patients with severe joint damage, allowing them to resume their normal activities and enjoy a better quality of life.
3. Long-Term Durability:
- Modern joint replacement devices are designed to be durable and long-lasting, providing years of reliable performance.
4. Minimally Invasive Techniques:
- Advances in surgical techniques, such as minimally invasive surgery and robotic-assisted surgery, have reduced recovery times and improved outcomes for patients undergoing joint replacement surgery.
5. Customization:
- Joint replacement devices can be customized to fit the unique anatomy and biomechanics of each patient, ensuring optimal fit and function.
Conclusion
Joint replacement devices have revolutionized the treatment of joint-related conditions, offering relief to millions of people suffering from debilitating joint pain and limited mobility. With different types of joint replacement devices available, including total hip replacement, total knee replacement, total shoulder replacement, and partial joint replacement, patients have options for restoring function and alleviating pain in damaged or diseased joints. By understanding the types, benefits, surgical procedures, and postoperative care associated with joint replacement devices, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment options and achieve the best possible outcomes for their joint health and mobility.